Ask Me Anything by Pau Waelder
Ask Me Anything is a series of articles in the form of conversations, aiming to clarify certain terms, techniques, and debates related to digital art. Our Senior Curator puts 20 years of expertise in digital art at your service to answer your questions, taking only 5 minutes of your time.
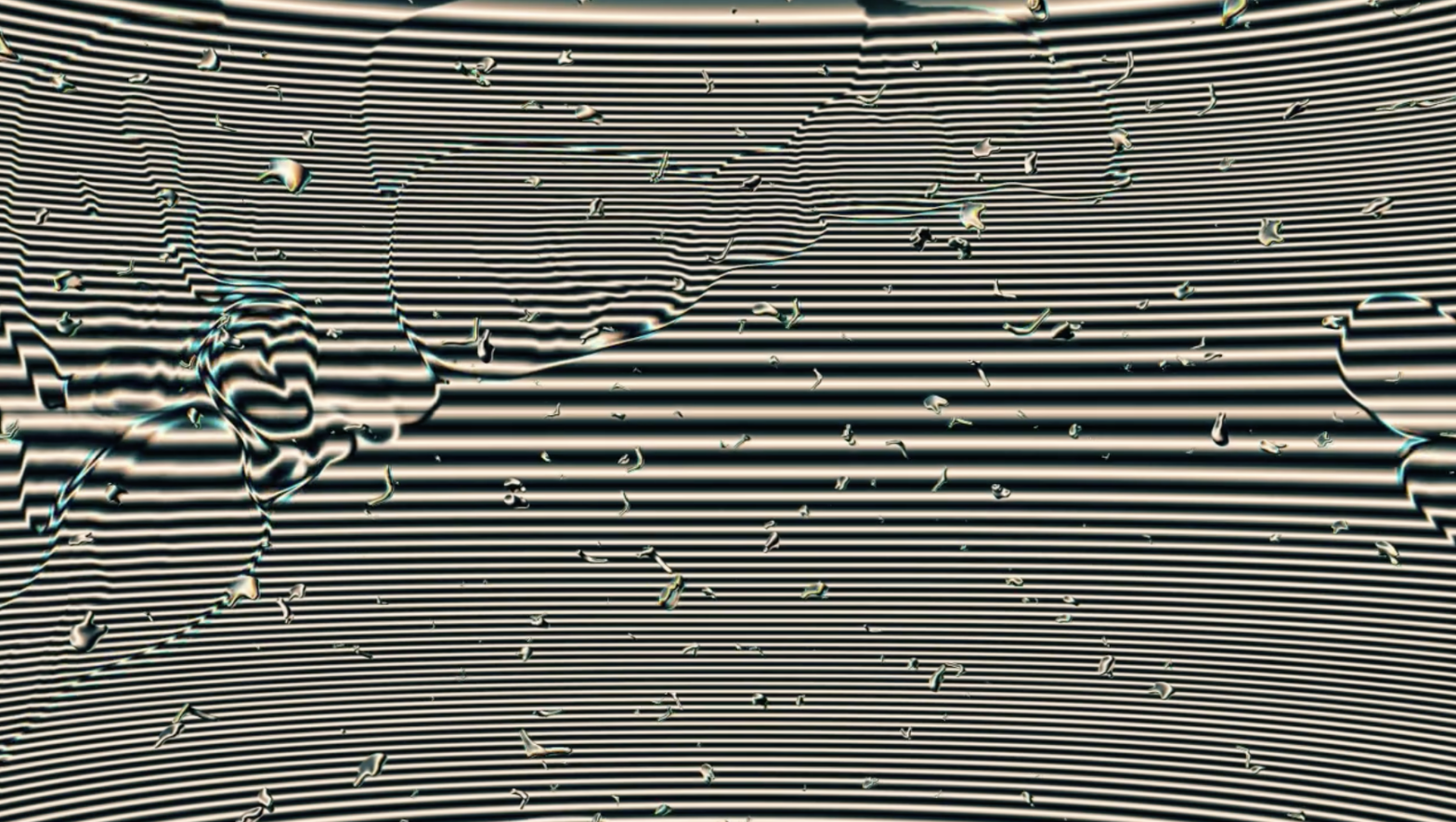
Mark Amerika. Mobile Beach, 2007
Hey, what happened? The screen is broken!
What? Ah, don’t worry, the screen is fine. What you are seeing is glitch art.
This is art? But there’s something wrong with the image, it’s not loading properly. Did you check the cables?
Yes, precisely that is how the image is supposed to look. The glitches are what this type of art is about.
Oh, you can’t be serious… How can this…? I mean, ah… I can’t concentrate with this image jumping around and… and getting all pixelated and broken…
I understand. Let me recommend a simple exercise: take a deep breath… and stop trying to fix the image, just look at the changing patterns on the screen. Don’t think of it as an image of a river, or the portrait of a woman, or whatever it is you are trying to see there. That is just an illusion. The image does not exist, it is just information interpreted by a program and displayed on a screen.
The image does not exist, it is just information interpreted by a program and displayed on a screen.
I don’t understand. When I download an image to my computer, it is always an image. I see a thumbnail on the desktop, I click on it, and there it is: an image.
Yes, because it is interpreted as such every step of the way by the operating system. But try this simple trick:
1. Click on the filename. Change the extension from .jpg or .png to .txt
2. Open the file. The operating system will use a text editor.
3. You’ll see strings of weird characters that make no sense. Select some and erase them.
4. Save the file. Change the extension back to .jpg or .png
5. Open the file. The image has changed, it is probably broken or cut at some point.
This shows you what I explained before. When everything goes well, you are deceived into seeing a sharp, beautiful image, but when the data is corrupted, not properly transmitted, or there is an error in the program interpreting the data, this is what happens.
Ok I get it. But then, why is this art?
Glitch art is mainly about exploiting an error in a computer system, exposing its inner workings. It is hard to offer a specific definition, since there are many types of glitches and ways of interpreting what a “glitch” can be. Artist and researcher Rosa Menkman, who has extensively worked and theorized about glitch art, puts it this way:
“A glitch is the most puzzling, difficult to define and enchanting noise artifact; it reveals itself to perception as accident, chaos or laceration and gives a glimpse into normally obfuscated machine language. Rather than creating the illusion of a transparent, well-working interface to information, the glitch captures the machine revealing itself. Glitch artists make use of the accident to ‘disfigure’ flow, image and information, or they exploit the void – a lack of information that creates space for deciphering or interpreting the process of creating (new kinds of) meaning.” [1]
Menkman argues that glitch art goes beyond the aesthetic or the machinic, revealing flaws that are also present in social, political, and knowledge systems.

How can art be about error and nonsense?
Different art movements have explored the creative potential of errors and played with the absurd. Take for instance the Dadaists, who proclaimed the futility of art and their distrust of the art system. “Everything one looks at is a fake,” said Tristan Tzara in his Dada Manifesto of 1918. The Surrealists also wanted to disrupt the creative process and access less formal and rational ways of creating art by introducing randomness and spontaneity.
Ok, but the Dadaists and Surrealists did not use computers.
No, but they faced structured systems with codes and an internal logic that they wanted to disrupt. Using random words to create a poem or creating one out of unintelligible words, such as “dll rrrrr beeeee bö fümms bö,” as Kurt Schwitters did in his Ursonate (1932), is akin to creating a glitch in language, understood as a formal system, and actually developing a different kind of language. Similarly, Glitch Art is not simply about creating a disruption in a computer system, but exploring the creative and expressive capabilities of integrating glitches into a digital image, video, text, sound, or software, among other mediums.
Hold on, you’re saying that the artists create the glitches?
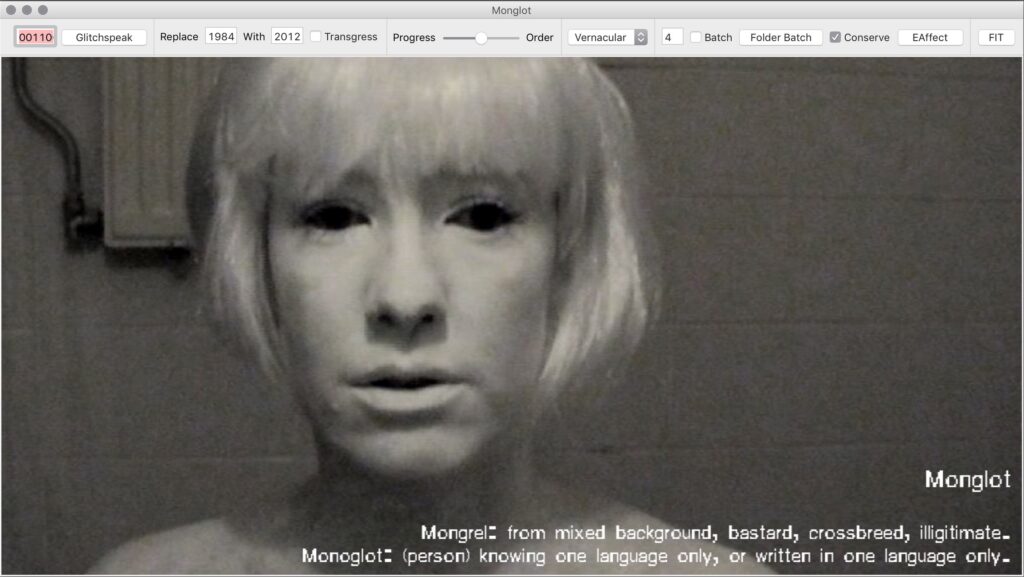
They sometimes appropriate them, or create the conditions for the glitches to happen. Musicians working with electronic synthesizers already experimented with disrupting the circuits to create noise. Also artists like the duo JODI, who are among the pioneers of net art, explored the aesthetic capabilities of the code hidden behind every website and also with the first modifiable versions of videogames such as Wolfenstein 3D or Quake. Some artists appropriate glitches happening while using computer software, as for instance Ant Scott, who in the early 2000s built a blog collecting screenshots and photos of software crashes and offered an initial definition of glitch art. Others initiate a process aimed at making glitches happen: this is the case of Mark Amerika’s experiment with mobile video in the late 2000s, forcing the capabilities of the mobile phone and the limitations of streaming HD video to generate “datamoshing,” a visible error caused by video compression. Rosa Menkman and Johan Larsby created in 2011 a glitch generator software called Monglot as a way of teaching about glitch at a moment in which it had been widely adopted as a purely aesthetic visual style in music videos and graphic design. More recently, glitch has been frequently adopted in the NFT art scene, as can be found in the work of Domenico Barra, or notably in generative art projects such as Kim Asendorf’s Sabotage. Then some artists are inspired by glitch art but move beyond it, as is the case of Yoshi Sodeoka, whose work connects noise music and glitch into an audiovisual language of his own.
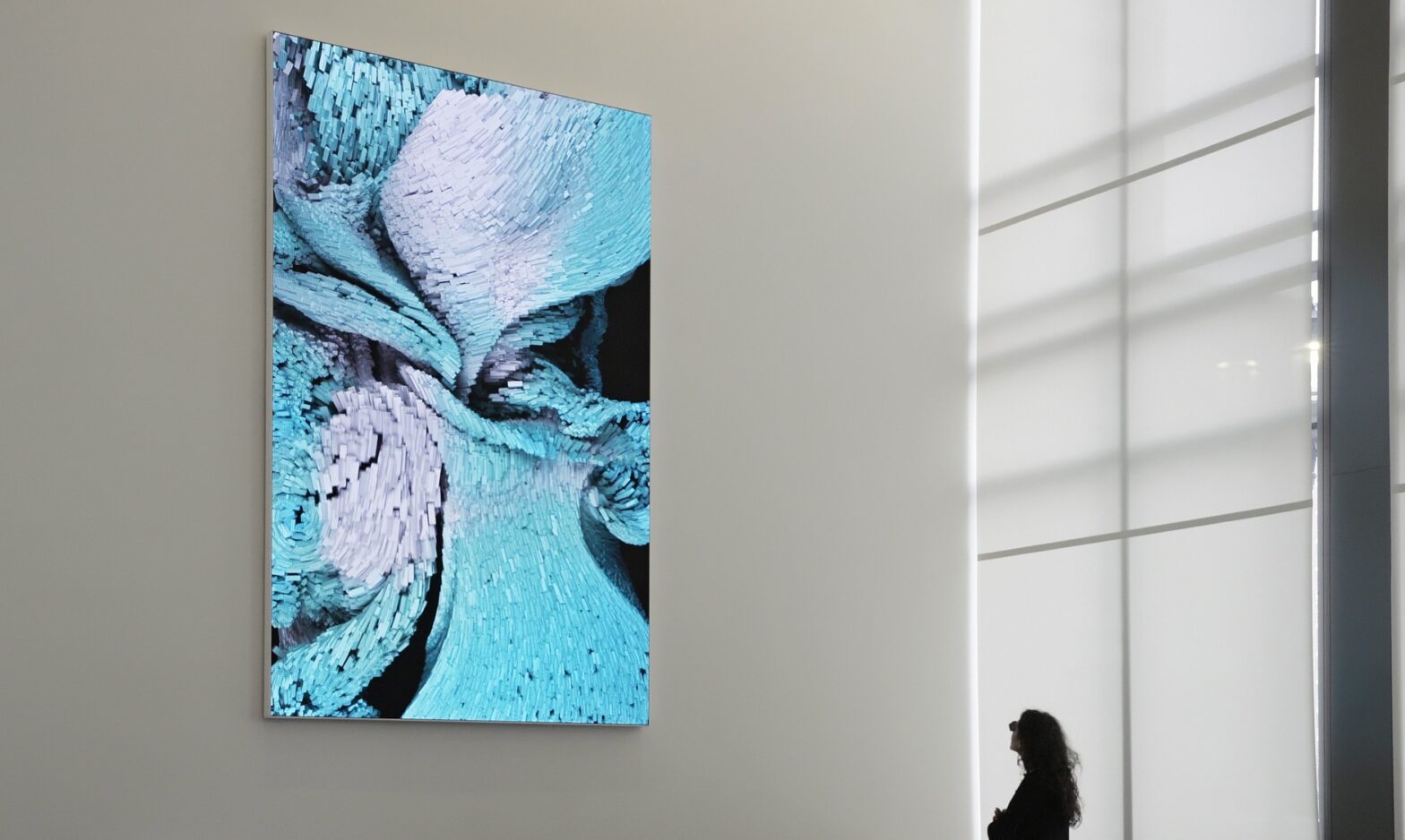
Yoshi Sodeoka, Synthetic Liquid 7, 2022.
Wow, you went full art historian mode there.
I just scratched the surface.
Understood, but now that we have increasingly better high resolution screens, hyperrealistic 3D simulations, and immersive virtual reality devices, what’s the point of glitch? Isn’t it a bit nostalgic and passé?
I would argue quite the opposite, that as the means to create a convincing virtual reality around us are getting better, we need to counter this sleek, fake hyper-reality with a bit of glitch. Besides, glitch is fun.
Yes, I have to say that once you “get it,” it’s quite fun.
Told ya.
[1] Rosa Menkman. The Glitch Moment(um). Amsterdam: Institute of Network Cultures, 2011, p.29-30, 33.